The electric vehicle (EV) sector is gaining momentum in India as the country pushes towards a cleaner and more sustainable future. A recent study by the India Energy Storage Alliance (IESA) revealed that the total EV sales in 2018 hit 365,920 units and are expected to grow at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 36% till 2026. The EV battery market in India is estimated to be US$ 520 Million in 2018 and is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 30% by 2026.[1] The study also notes that the government’s push towards electrification, coupled with favourable policies and incentives, is expected to boost the adoption of EVs in the country.
REASONS FOR SHIFT TOWARDS EV-SECTOR
- Rising pollution levels– In COP21, India committed to reducing the emission intensity of its GDP by 33-35% by 2030. At present, 97% of Indian vehicles are propelled by petrol and diesel which have an adverse impact on the environment. [2] Therefore, India needs to shift towards greener mobility technologies in transport like EVs that could help in mitigating the adverse environmental impacts caused by conventional vehicles.
- Rising Crude Oil Imports- India’s crude oil imports have risen exponentially making India 3rd largest consumer of crude oil. India needs to swiftly move away from conventional vehicle technology to avoid higher import dependency which is possible only by giving a push to the EV sector.[3]
- Rising Population– A sustainable mobility challenge India’s current population of 1.2 billion is expected to reach 1.5 billion by 2030. 40% of the population is expected to live in urban areas, it is likely to put pressure on the struggling urban infrastructure in the country, including a rise in demand for sustainable mobility solutions
IP AND EV SECTOR
Several Indian companies have also filed patents related to electric vehicles in recent years. For example, Tata Motors, India’s largest automaker, has filed patents related to EV battery management systems and electric motor technology. Mahindra & Mahindra, another major Indian automaker, has filed patents related to EV battery cooling systems and regenerative braking technology. Electric Vehicles are the future of the global automobile sector. There will be innumerable patents filed in the innovative field related to EVs such as batteries, motors, controllers, chargers, and testing equipment for EVs. As the popularity of electric vehicles grows, manufacturers will continue to improve their battery technology and vehicle infrastructure. In-vehicle changes such as engine control systems and new filtering technologies will also create patenting opportunities. Traditional automotive businesses are reacting by increasing their investment in R&D to stay on top of electrification.
Patents related to battery technology – The focus on, and growth of EVs have led to greater innovation in battery technology. There is an immediate imperative for the government to push for carbon reduction especially, vehicular emissions. Many patents have been filed related to energy storage that is focused on improving battery technology.
Patent for EV charging station – The adoption of EVs has led to increased patents for charging infrastructure including wireless EV charging. That said, even the charging stations will need backups because we still grapple with power cuts in India.
Design rights and copyright – Electric vehicles have evolved to accommodate batteries and to become lighter and more aerodynamic. Protecting the changing shape and design of vehicles will become increasingly important to safeguard that investment. For instance, Tesla introduced a fire suppressant in its recent model to avoid heating of the battery, which is a common issue in summer and leads to battery explosions. These kinds of innovations and designs would need proper IP protection.
Patent data for the EV sector confirms that electric vehicles as a sector has tremendous scope to contribute to the future of mobility. To promote patent filings in the EV sector the Modified Special Incentive Package Scheme (M-SIPS)[4], the scheme has been extended to cover the EV sector, providing financial incentives for companies to invest in research and development in the field and to file patents for innovations.
PATENT FILING TRENDS FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLE
According to the recent patent filing trend for the EV technology, USA and China were the world leaders with total filing of 3,84,840 and 1,78,300 respectively between the year 2016-2022. The United States of America and China are the top regions in the world conducting most research in the field of EVs. The applicants also use alternative paths or routes for filing their patent applications like the European patent office and Patent cooperation treaty to seek protection in several countries by single and first filing.
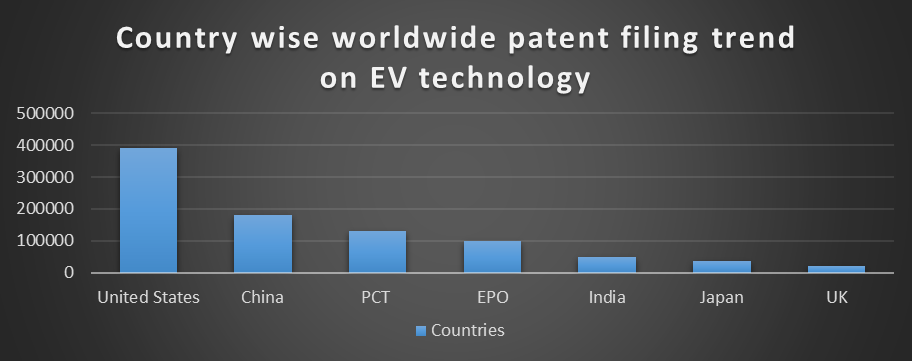
(Source: PATENSCOPE database)
CHALLENGES
- Infrastructure- The challenges faced by the EV industry in India would include the lack of charging infrastructure, limited availability of EV models, and high upfront costs. Further, the domestic infrastructure of EVs needs to cater to the needs of the common man.
- Design and Efficiency- Further, it will become important to increase the efficiency of these models and for this, there would be the development of new designs for electric vehicles which would lead to more design patents being filed. Thus, it would be a challenge to not only differentiate in designs but also the promptness in filing for the same by the applicants.
- Tech Upgradation- EV and technology systems should work hand in hand. There should be the development of apps to monitor the battery percentage, nearby charging stations, health of the vehicles. This would also be a challenge to make these vehicles tech-savvy.[5]
- IP Awareness- However, the EV sector in India faces several challenges, such as a lack of awareness among inventors and companies about the importance of patent protection and the high cost of obtaining and enforcing patents. The government has taken steps to address these challenges, such as launching awareness campaigns to promote patent filing and introducing fast-track examination of patent applications for select sectors, including the EV sector. Thus, protecting Intellectual Properties and defending them will become necessary for all the players in the EV space.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
- The National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020 [6]– FAME-I Scheme [1st April 2015 – 31st March 2019]: India has set an ambitious target of achieving 30% electric mobility by 2030, which includes both electric vehicles and charging infrastructure. The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles in India (FAME India) Scheme was developed by the Department of Heavy Industry in 2015 to promote the production of electric and hybrid vehicle technologies and ensure its sustainable growth by providing financial incentives for the purchase of EVs.
- FAME-II Scheme [1st April 2019 – 31st March 2024]: Phase-II of the FAME Scheme attempts to create demand for Electric Vehicles (EVs) in the country and promote the creation of charging infrastructure. Its emphasis is on providing economical and environment-friendly public transportation options for the public.[7]
- PLI Scheme [Duration of 4-6 years]: The Government of India approved the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme[8] for the Indian Automobile and Auto Component Industry to improve India’s manufacturing capabilities. Its primary objectives are to overcome economic constraints, generate economies of scale, and establish a reliable supply chain for Advanced Automotive Products (AAT) products.
- The Hon’ble Finance Minister in her Budget Speech of 2022–23 announced that the Union Government would introduce a Battery Swapping Policy[9] to improve efficiency in the EV ecosystem. Battery Swapping is when a battery swapping station will enable an electric vehicle (EV) owner to quickly swap out a dead battery for a charged one.
CONCLUSION
Intellectual Property play a vital role in promoting innovation and driving economic growth in the EV sector in India. The government has recognized the importance of patents in promoting the development of the EV sector and has introduced several initiatives to encourage patent filings and promote research and development in the field. Continued efforts to address the challenges faced by the patent system in India can help ensure that the EV sector continues to drive innovation and economic growth in the country. the study highlights the significant potential of the EV sector in India and the need for continued government support and private-sector investment to unlock this potential. The adoption of EVs can not only help India achieve its climate goals but also create new opportunities for businesses and drive economic growth.
[1]https://indiaesa.info/media/downloadfiles/EV_Report_Brochure._234429529.pdf
[2]https://www.niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/202104/FullReport_Status_quo_analysis_of_various_segments_of_electric_mobility-compressed.pdf
[3]https://beeindia.gov.in/sites/default/files/press_releases/2019%20-%20EY%20to%20BEE%20%20Technical%20study%20on%20EVs%20%26%20Charging%20Infrastructure.pdf
[4]https://www.meity.gov.in/esdm/incentiveschemes#:~:text=The%20Scheme%20provides%3A,date%20of%20approval%20of%20application.
[5]https://www.niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/202104/FullReport_Status_quo_analysis_of_various_segments_of_electric_mobility-compressed.pdf
[6]https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1577880
[7]https://indiaesa.info/images/Resources/Webinar_Slides_2022_India_EV_Charging_Infrastructure_Market_Report.pdf
[8] https://www.meity.gov.in/esdm/pli
[9] https://www.niti.gov.in/draft-battery-swapping-policy

